过渡金属硫化物Transition metal dichalcogenides(TMDs)薄到单原子层厚度时,能带结构从间接带隙变成直接带隙,拥有优异的光、电性能,在微纳光子器件中具有重要的应用。然而,单层TMD厚度(0.62nm)限制了光与它的相互作用,导致荧光发光强度和量子效益较低,现在了它的应用。武山课题组设计了一种悬空的TMD-SiN-Ag结构,利用超薄的氮化硅把二硫化钼和金属微纳结构分开,既避免了TMD和金属结构的相互污染,又利用金属结构的等离激元共振有效的增强了二硫化钼的拉曼和荧光信号,平均发射的荧光强度提高了2个数量级,比大部分文献中报道的效果要好。此外,通过数值模拟和实验结果对比,获得出了金属结构量子效益提高的数据。研究结果发表在中科院一区SCI杂志Nanophotonics 10, 975-982 (2020)。文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2020-0545。

Figure 1.(a) Scheme of the sample preparation process. (b) top-view scanning electron micrograph of the hybrid structure with period of 260 nm. That pointed by blue arrow is a crack of monolayer MoS2. (c) Raman spectra of monolayer MoS2on the perforated metallic structure (black solid line) and SiN/Si substrate (red dash line). A characteristic peak of silicon (520.7 cm-1) appears in Raman spectrum on the substrate.
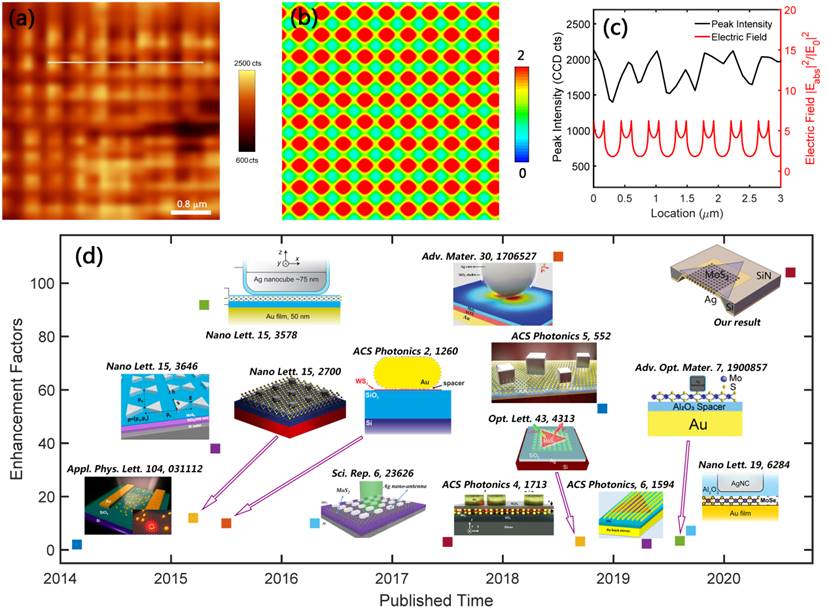
Figure 2.The measured A-excitonPL intensitymapping (a) and calculated total electric field distributions (b) of themonolayer MoS2loaded SPM structure withP= 440 nm, respectively.(c) The A-excitonPL peak intensity (black)and electric field intensity (red) profiles along the indicated white line in (a). (d)Comparison of PL enhancement factors of different plasmon based PL enhancement strategies in the past five years.Note that all enhancement factors shown in (d) are actual results of experimental measurement (not be normalized by the area of single nanocavity).